Example Use Case
Choosing Materials
The Quick Start Guide showed how a user could quickly examine the galvanic impact of a dissimilar material couple. In this section we will build upon the first material couple and illustrate how a user can make informed choices of materials, coatings and treatments in order to mitigate corrosion risks.
For demonstration purposes let’s imagine a scenario where an engineer has to specify a material for bushings to be used in an airframe repair. Over time, fixture systems (bolts, fasteners, etc) connecting components to airframes may cause the airframe to corrode. The repair procedure would comprise the removal of corroded material and restoring the fixture hole diameter by use of a bushing. The material choice for the bushing is very important as a poor material choice may lead to galvanic corrosion risk.
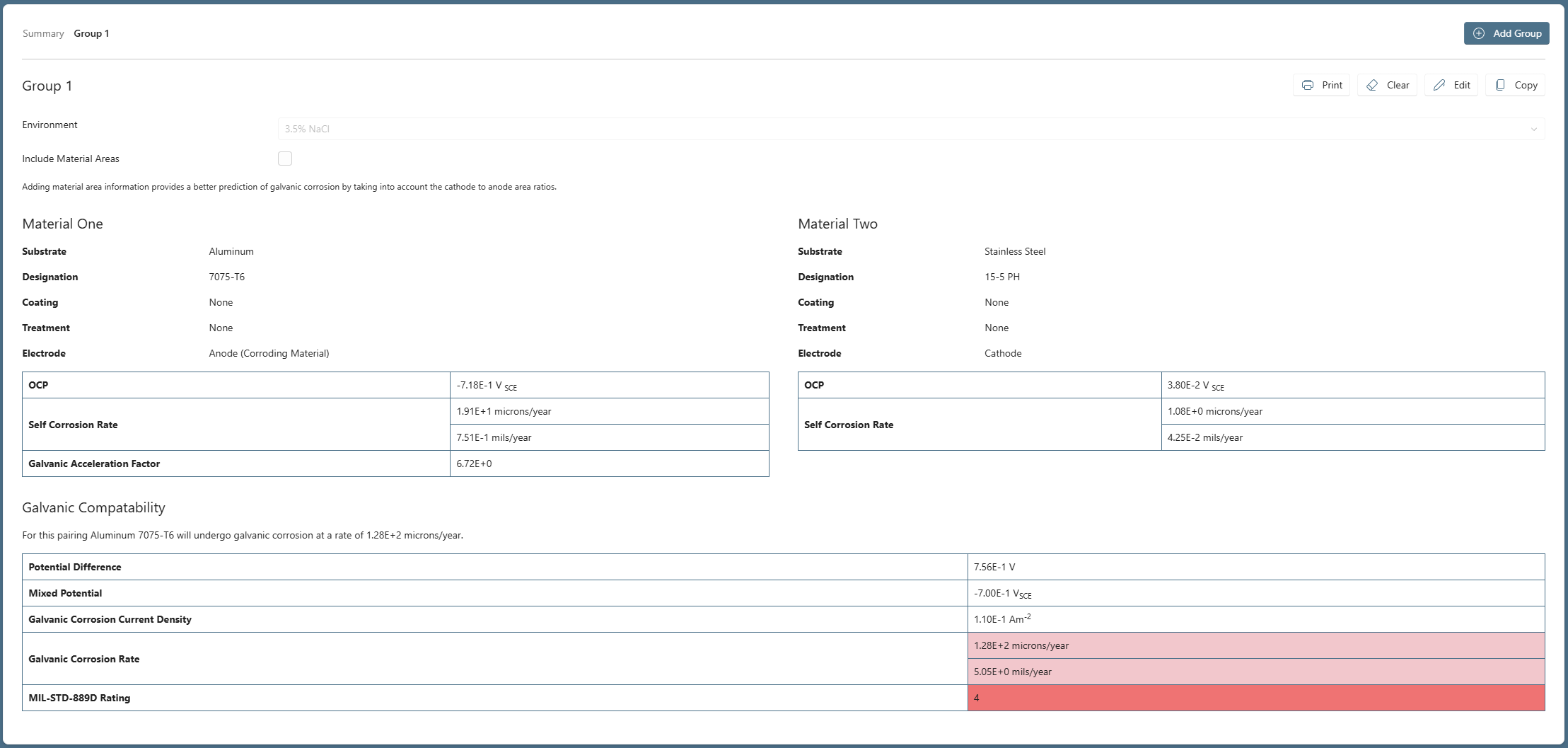
Our first group, already examined corresponds to the proposed use of Stainless Steel 15-5 PH bushings in an airframe structure comprising Aluminum 7075-T6.
Adding a Coating
Question
What would be the impact of anodizing the Aluminum 7075-T6, but staying with the bushing material of Stainless Steel 15-5 PH?
To examine this the user simply clicks ‘Copy’ and a second group is created as a second ‘TAB’ with the same materials pre-populated. The user then changes the selections for the Aluminum 7075-T6, assigning an anodize (BSAA) for the coating and an ‘Anodize Seal Chromate 6+’ for the treatment, see Figure 2.
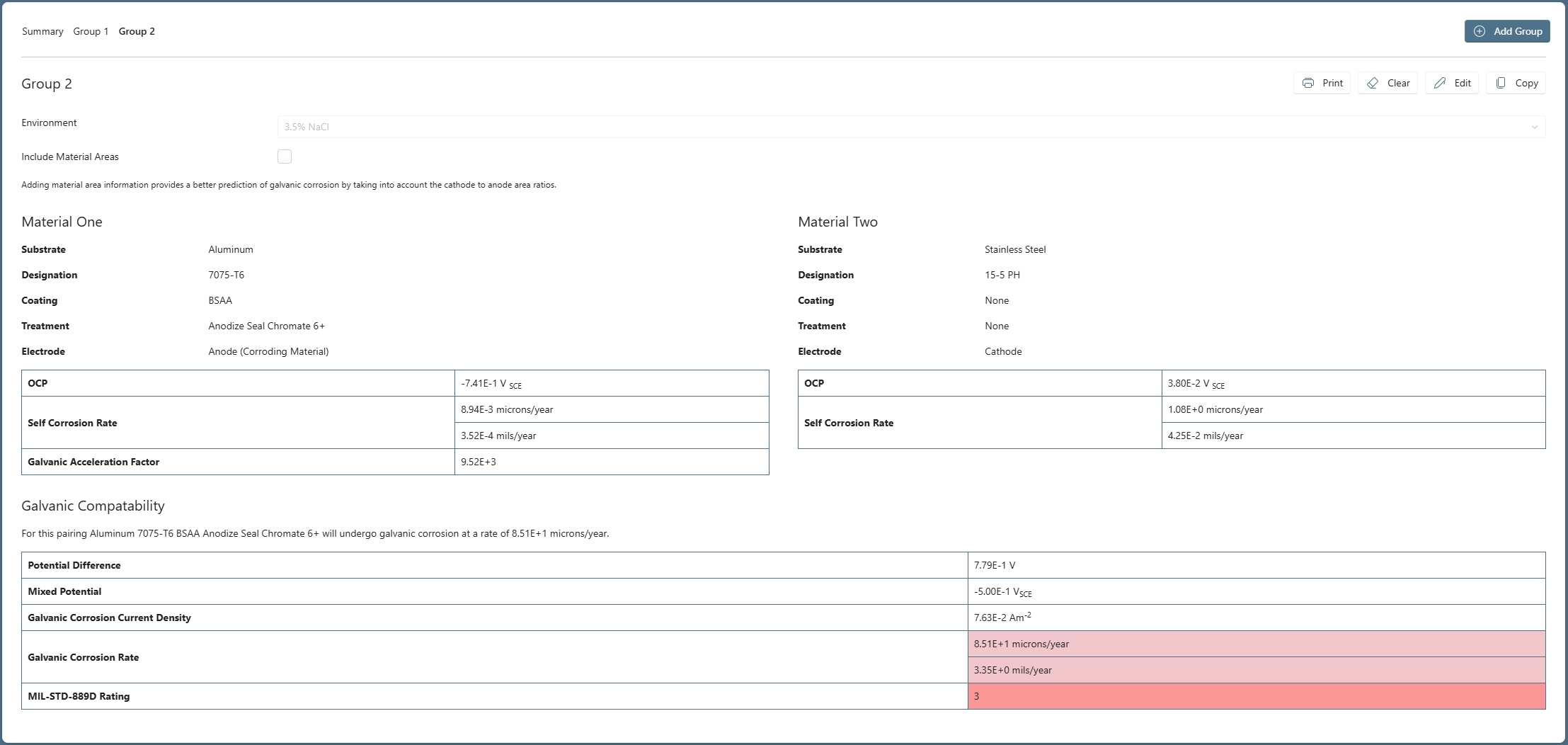
As expected, anodizing dramatically drops the self-corrosion rate of the Aluminum 7075-T6 to fractions of a micron per year. However, when coupled to the Stainless Steel 15-5 PH the galvanic corrosion rate is still high, at a value of 85.1 microns/year.
So, anodizing the anodic member of this particular couple has had little impact on galvanic corrosion. Another approach would be to consider treatments for the cathodic member, in this scenario, the Stainless Steel bushing.
Alternative Material Choices
So, while on the Group 2 TAB, we click ‘Copy’ to create Group 3 and change the Material 2 descriptors to a Titanium, Ti6Al4V when done, click 'Run Analysis', the results are shown in Figure 3.
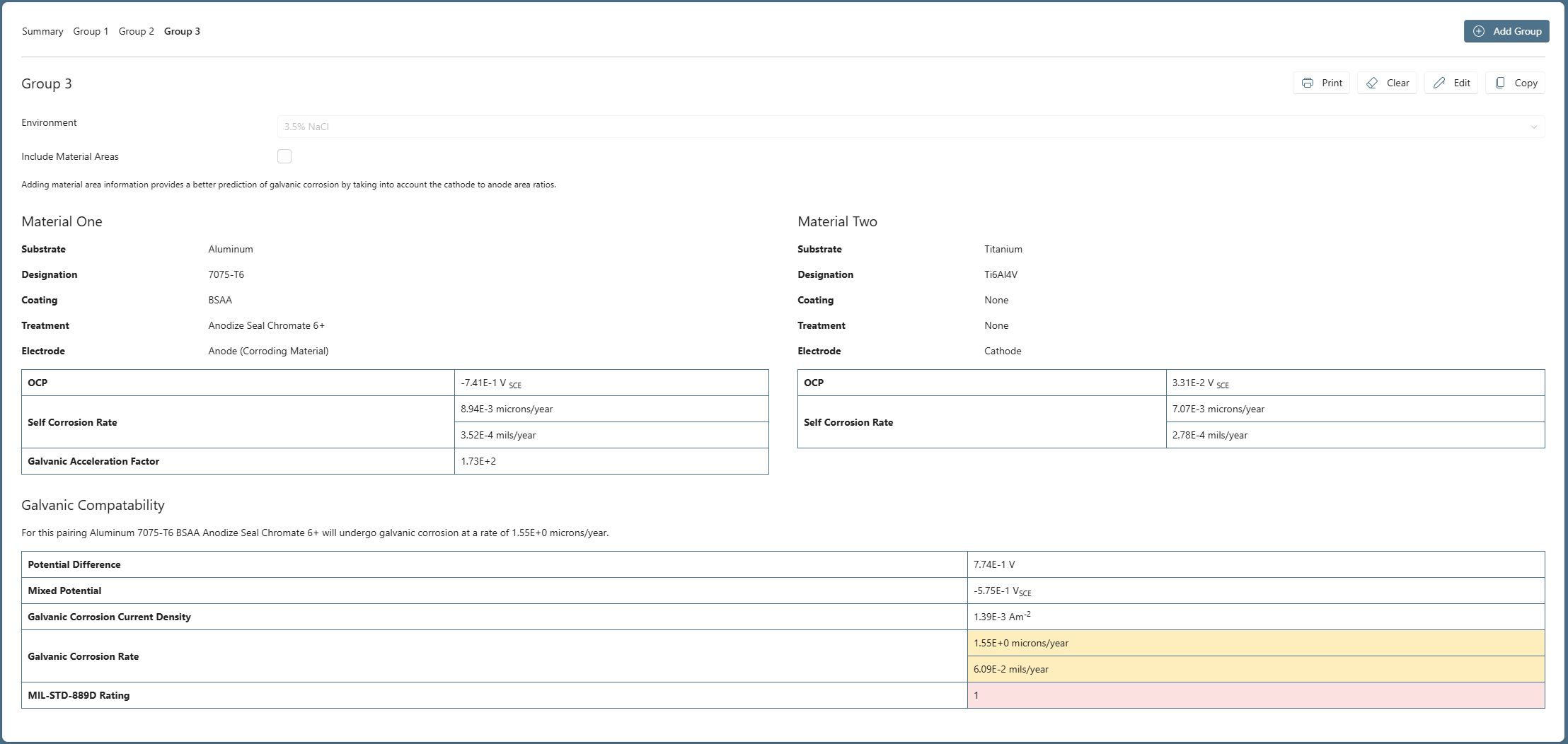
The use of the Titanium, Ti6Al4V results in a significantly lower Galvanic Corrosion Rate of 1.55 microns/year, despite the similar potential differences between the material couples.
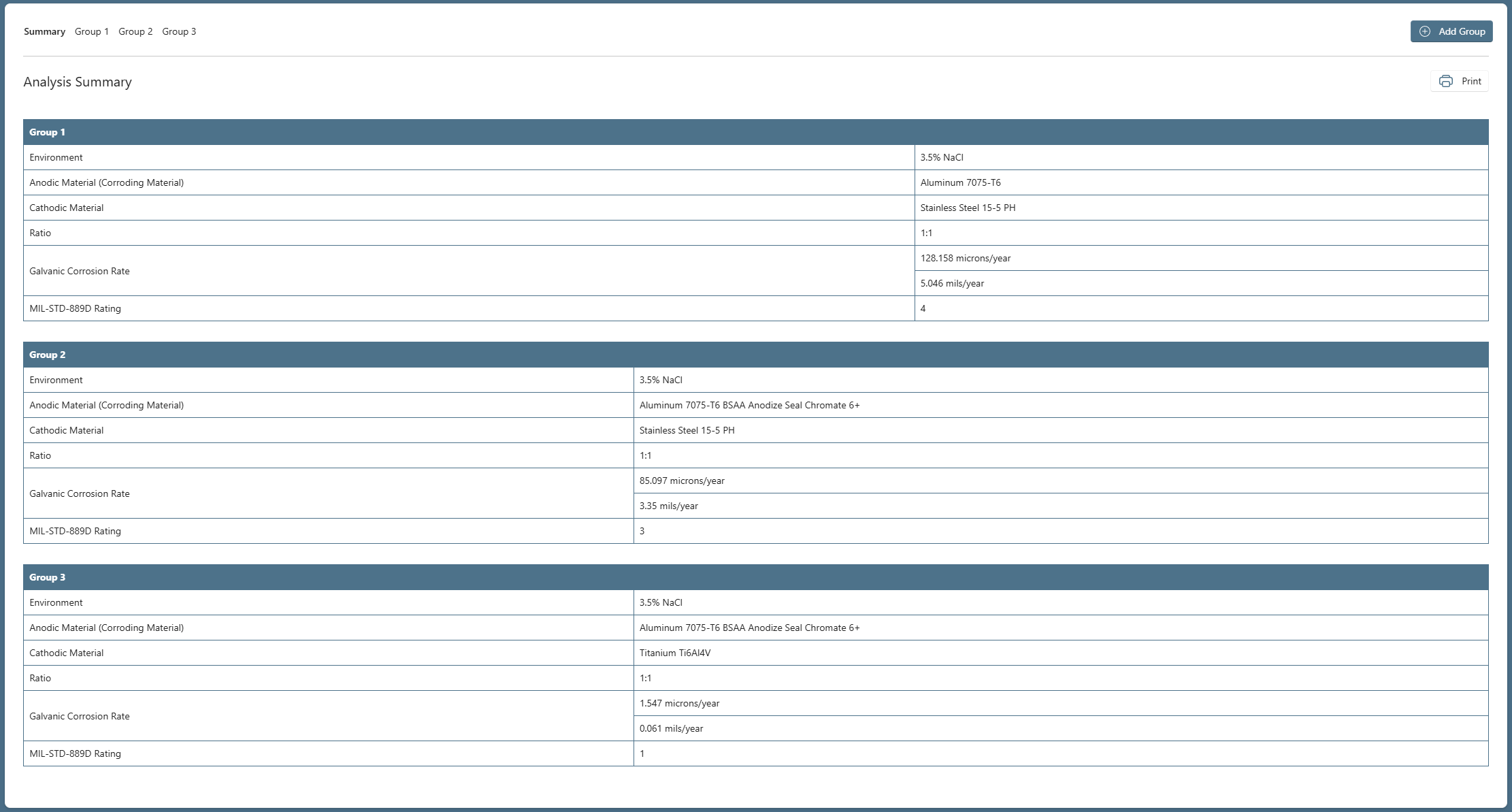
Analysis Summary
A summary of the Analysis can be seen in Figure 4 which shows the change in Galvanic Corrosion Rate as we updated our material choices.